Remove Duplicates with Dictionary
DOWNLOAD USED EXCEL FILE FROM HERE>>
In today’s post, we will explain you How to Remove Duplicates with Dictionary using Excel VBA, Excel has a feature which is used for remove duplicates with dictionary the selected cells, rows or table. By the way, we can remove duplicates manually also, but today we will Remove duplicates with dictionary the help of VBA, if we automate this process in VBA. Yes, the process of remove duplicates can be automated in VBA as a macro. In the process of remove duplicates, once this is done the unique values remain in the list or table. This can be done with the help of the Remove Duplicates function in VBA.
You can see below that we will remove duplicates with dictionary.
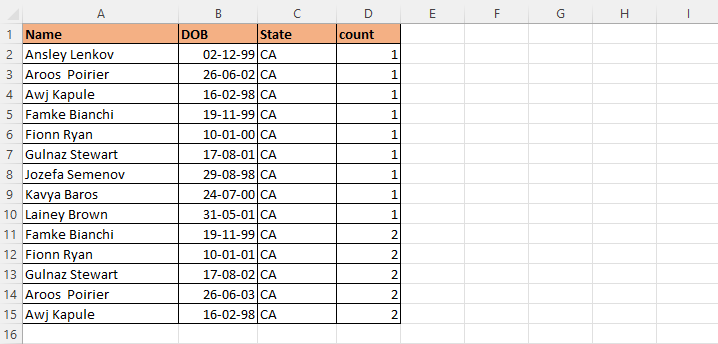
Let us now understand How to Remove Duplicates with Dictionary using Excel VBA
Remove Duplicates with Dictionary using Excel VBA
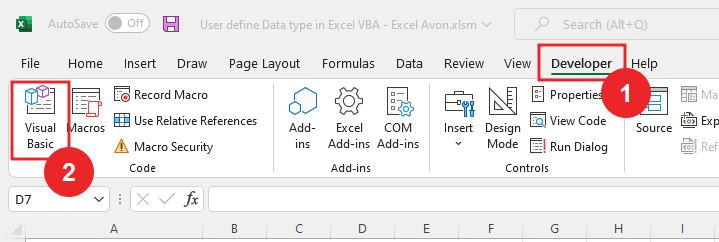
Well, you must know that How to Remove Duplicates with Dictionary using Excel VBA we will learn in this article. VBE’s, let’s understand. So, we have to go like last time, first go to the Developer Tab then click on the option of Visual Basic as shown in the image below.
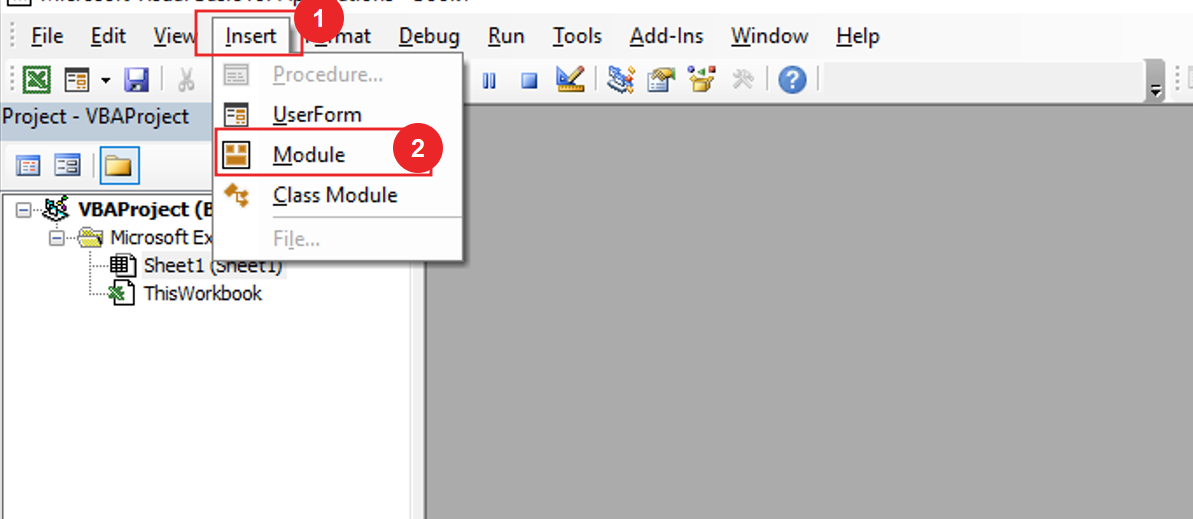
On opening in VBE, you have to go to Insert and then Module has to be inserted, as can be seen in the image.
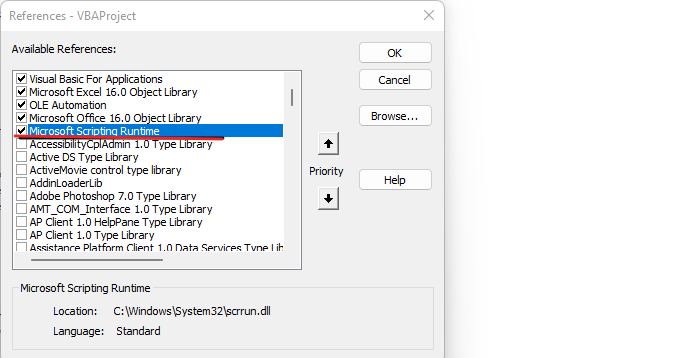
Microsoft Runtime Library must be activated to when using dictionary. to activate go to Tools option and then References and on that we select Microsoft Script Runtime Library and click OK.
Once the module is inserted, and the library is activated, we’ll write a subroutine to Remove Duplicates with Dictionary.
Sub RemoveDuplicates() End Sub
Declaring more variables which are using in the entire project for Long, Variant, worksheet, and Range.
Sub RemoveDuplicates() Dim Lr As Long, Dim i As Long Dim dtArr As Variant Dim WS As Worksheet Dim dRng As Range 'Rng to delete Dim Ky As Variant End Sub
Here we are Declaring Instant variables for Dictionary.
Sub RemoveDuplicates() Dim Lr As Long, Dim i As Long Dim dtArr As Variant Dim WS As Worksheet Dim dRng As Range 'Rng to delete Dim Ky As Variant Dim Dic As New Dictionary End Sub
Now we will set worksheet as ActiveSheet.
Sub RemoveDuplicates() Dim lr As Long, i As Long Dim dtArr As Variant Dim WS As Worksheet Dim dRng As Range 'Rng to delete Dim Ky As Variant Dim Dic As New Dictionary Set WS = ActiveSheet End Sub
Here we will Declare last row.
Sub RemoveDuplicates()
Dim lr As Long, i As Long
Dim dtArr As Variant
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim dRng As Range 'Rng to delete
Dim Ky As Variant
Dim Dic As New Dictionary
Set WS = ActiveSheet
lr = WS.Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
End Sub
Here we will Declare Array Range
Sub RemoveDuplicates()
Dim lr As Long, i As Long
Dim dtArr As Variant
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim dRng As Range 'Rng to delete
Dim Ky As Variant
Dim Dic As New Dictionary
Set WS = ActiveSheet
lr = WS.Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
dtArr = WS.Range("A2:D" & lr).Value
End Sub
Then we will define key Array, here we will use UBound and LBound in Range.
Sub RemoveDuplicates()
Dim lr As Long, i As Long
Dim dtArr As Variant
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim dRng As Range 'Rng to delete
Dim Ky As Variant
Dim Dic As New Dictionary
Set WS = ActiveSheet
lr = WS.Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
dtArr = WS.Range("A2:D" & lr).Value
For i = UBound(dtArr, 1) To LBound(dtArr, 1) Step -1
End Sub
Then we will define key Array
Sub RemoveDuplicates()
Dim lr As Long, i As Long
Dim dtArr As Variant
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim dRng As Range 'Rng to delete
Dim Ky As Variant
Dim Dic As New Dictionary
Set WS = ActiveSheet
lr = WS.Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
dtArr = WS.Range("A2:D" & lr).Value
For i = UBound(dtArr, 1) To LBound(dtArr, 1) Step -1
Ky = dtArr(i, 1)
End Sub
Here we will create condition using if statement if any specified key is not present in dictionary object, then key will be added.
Sub RemoveDuplicates()
Dim lr As Long, i As Long
Dim dtArr As Variant
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim dRng As Range 'Rng to delete
Dim Ky As Variant
Dim Dic As New Dictionary
Set WS = ActiveSheet
lr = WS.Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
dtArr = WS.Range("A2:D" & lr).Value
For i = UBound(dtArr, 1) To LBound(dtArr, 1) Step -1
Ky = dtArr(i, 1)
If Not Dic.Exists(Ky) Then
Dic.Add Ky, ""
Else
End Sub
Else Another condition if dRng is nothing. then set dRng as worksheet which Range is from A to D.
Sub RemoveDuplicates()
Dim lr As Long, i As Long
Dim dtArr As Variant
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim dRng As Range 'Rng to delete
Dim Ky As Variant
Dim Dic As New Dictionary
Set WS = ActiveSheet
lr = WS.Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
dtArr = WS.Range("A2:D" & lr).Value
For i = UBound(dtArr, 1) To LBound(dtArr, 1) Step -1
Ky = dtArr(i, 1)
If Not Dic.Exists(Ky) Then
Dic.Add Ky, ""
Else
If dRng Is Nothing Then
Set dRng = WS.Range("A" & i + 1 & ":D" & i + 1)
Else
End Sub
After this, we will create another condition with which we will use the union function. Use union to combine two or more than two ranges.
Sub RemoveDuplicates()
Dim lr As Long, i As Long
Dim dtArr As Variant
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim dRng As Range 'Rng to delete
Dim Ky As Variant
Dim Dic As New Dictionary
Set WS = ActiveSheet
lr = WS.Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
dtArr = WS.Range("A2:D" & lr).Value
For i = UBound(dtArr, 1) To LBound(dtArr, 1)
Ky = dtArr(i, 1)
If Not Dic.Exists(Ky) Then
Dic.Add Ky, ""
Else
If dRng Is Nothing Then
Set dRng = WS.Range("A" & i + 1 & ":D" & i + 1)
Else
Set dRng = Union(dRng, WS.Range("A" & i + 1 & ":D" & i + 1))
End If
End If
Next i
End Sub
Another condition If there is any data after dRng combine, then the cell will be deleted and the cell will shift up. Use shifts up, when the data is deleted, the cell will shift upwards.
Sub RemoveDuplicates()
Dim lr As Long, i As Long
Dim dtArr As Variant
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim dRng As Range 'Rng to delete
Dim Ky As Variant
Dim Dic As New Dictionary
Set WS = ActiveSheet
lr = WS.Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
dtArr = WS.Range("A2:D" & lr).Value
For i = UBound(dtArr, 1) To LBound(dtArr, 1)
Ky = dtArr(i, 1)
If Not Dic.Exists(Ky) Then
Dic.Add Ky, ""
Else
If dRng Is Nothing Then
Set dRng = WS.Range("A" & i + 1 & ":D" & i + 1)
Else
Set dRng = Union(dRng, WS.Range("A" & i + 1 & ":D" & i + 1))
End If
End If
Next i
If Not dRng Is Nothing Then
dRng.Delete xlShiftUp
End If
End Sub
Run the code and see whether the Remove duplicates data or not.
Code is run and some duplicate value has been Remove. The data was up to 15 cell rows, but now after removing duplicates, up to 10 rows are left.
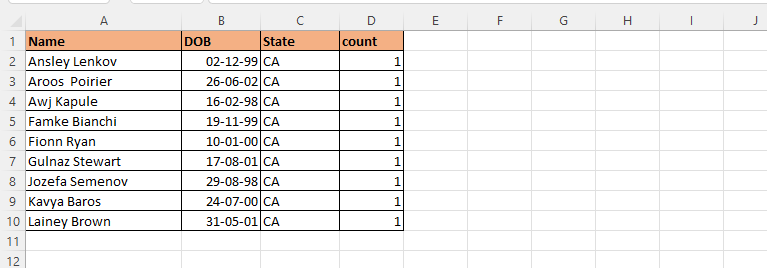
Back we will go to VBE and now we will combine and delete the two columns. Changes have been made in the code, that code is in bold font.
Sub RemoveDuplicates()
Dim lr As Long, i As Long
Dim dtArr As Variant
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim dRng As Range 'Rng to delete
Dim Ky As Variant
Dim Dic As New Dictionary
Set WS = ActiveSheet
lr = WS.Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
dtArr = WS.Range("A2:D" & lr).Value
For i = UBound(dtArr, 1) To LBound(dtArr, 1)
Ky = dtArr(i, 1) & vbTab & dtArr(i, 2)
If Not Dic.Exists(Ky) Then
Dic.Add Ky, ""
Else
If dRng Is Nothing Then
Set dRng = WS.Range("A" & i + 1 & ":D" & i + 1)
Else
Set dRng = Union(dRng, WS.Range("A" & i + 1 & ":D" & i + 1))
End If
End If
Next i
If Not dRng Is Nothing Then
dRng.Delete xlShiftUp
End If
End Sub
And Now Run Code

As you can see, by combining date and name from here, the data which was duplicated has been deleted. Here you can find only two value duplicate which got deleted.
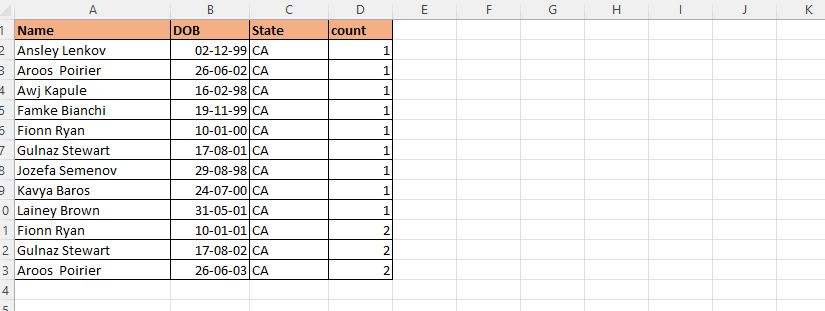
Again, we have to go to VBE and again backup the data and then we will Remove duplicates value which will be old and new ones will be saved. For this we do L bound later and U bound first, and we will apply to only one column here. And Step – 1 will be written after every step one step will decrease.
Sub RemoveDuplicates()
Dim lr As Long, i As Long
Dim dtArr As Variant
Dim WS As Worksheet
Dim dRng As Range 'Rng to delete
Dim Ky As Variant
Dim Dic As New Dictionary
Set WS = ActiveSheet
lr = WS.Range("A" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
dtArr = WS.Range("A2:D" & lr).Value
For i = LBound(dtArr, 1) To UBound(dtArr, 1) Step -1
Ky = dtArr(i, 1)
If Not Dic.Exists(Ky) Then
Dic.Add Ky, ""
Else
If dRng Is Nothing Then
Set dRng = WS.Range("A" & i + 1 & ":D" & i + 1)
Else
Set dRng = Union(dRng, WS.Range("A" & i + 1 & ":D" & i + 1))
End If
End If
Next i
If Not dRng Is Nothing Then
dRng.Delete xlShiftUp
End If
End Sub
Now we will run the code.

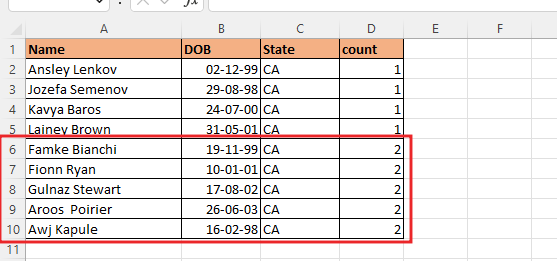
Now you can see here that the old data of all the duplicates has been deleted. In whose count you are seeing 2, the value has come for the second time, that means it is a duplicate value.
So, I hope you have understood How to Remove Duplicates with Dictionary using Excel VBA and for more information, you can follow us on Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, and YouTube as well.
DOWNLOAD USED EXCEL FILE FROM HERE>>
You can also see well-explained video here about How to Remove Duplicates with Dictionary using Excel VBA



